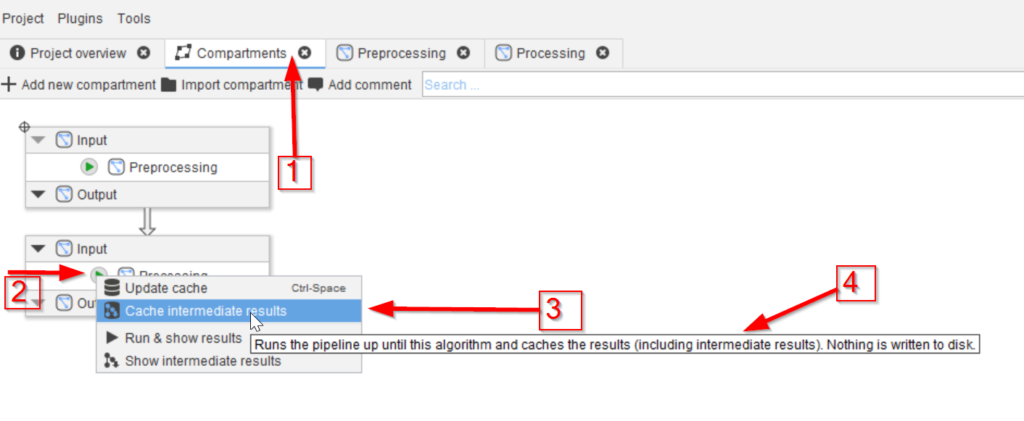
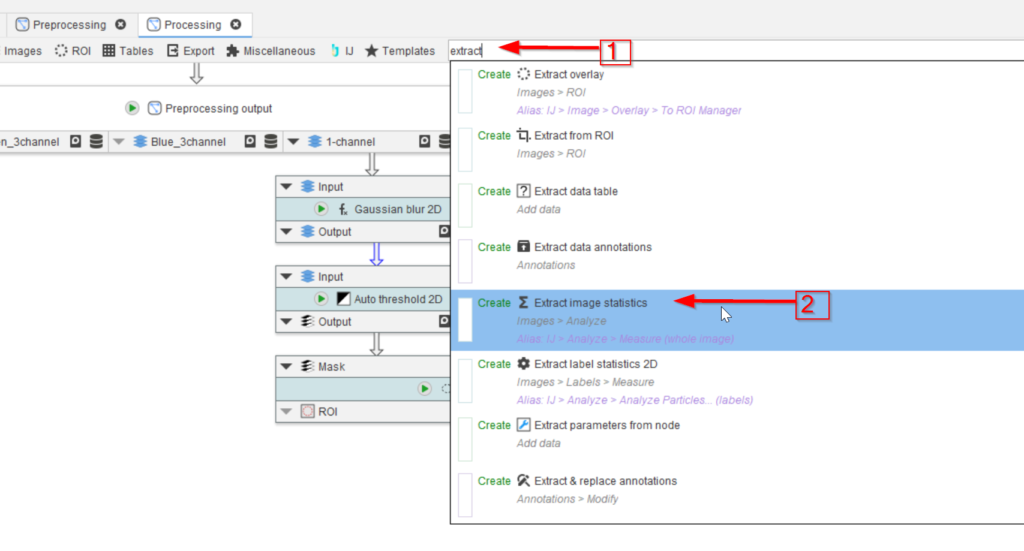
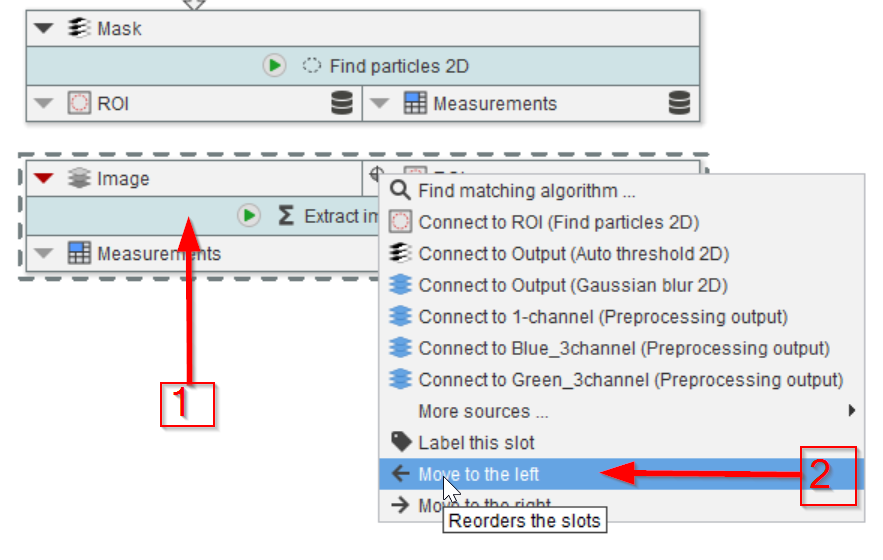
Step 3
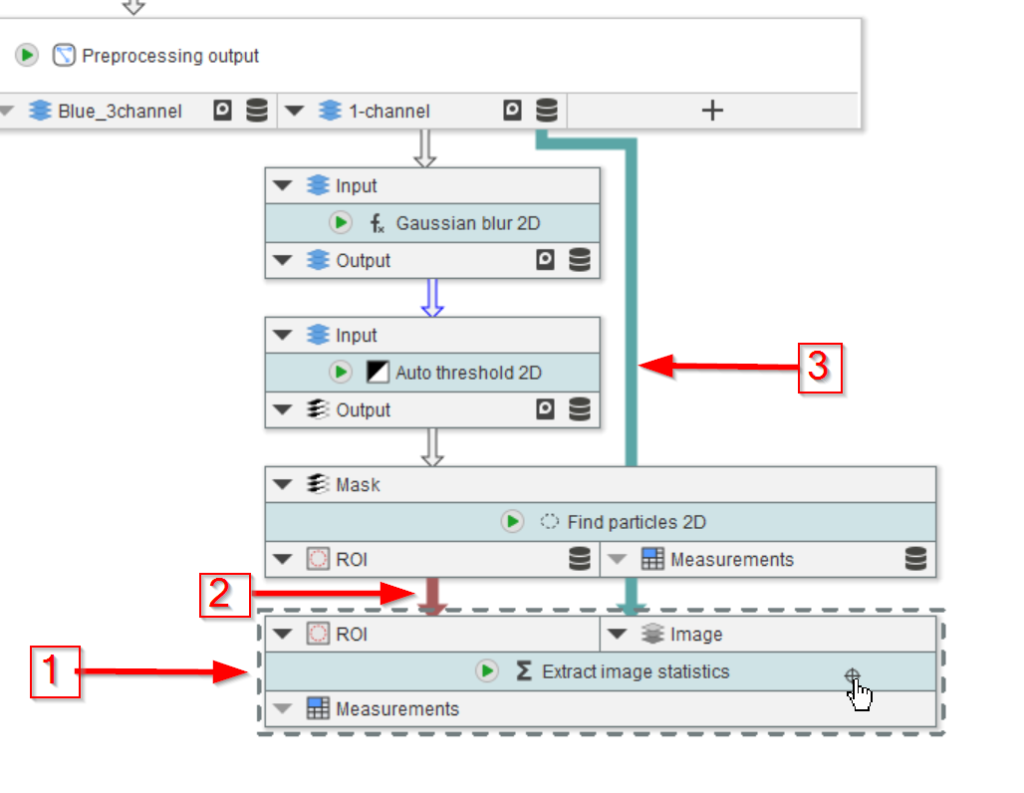
Look for nodes with the name extract (red arrow 1) and choose the Extract image statistics node (red arrow 2).
Step 4
Drag the new node to the UI and position it below the Find particles 2D node (red arrow 1). For convenience, rearrange to input slots of the new node by moving its right-side node to the left (red arrow 2) by clicking the ▼ button on the ROI slot and selecting Move to the left.
Step 7
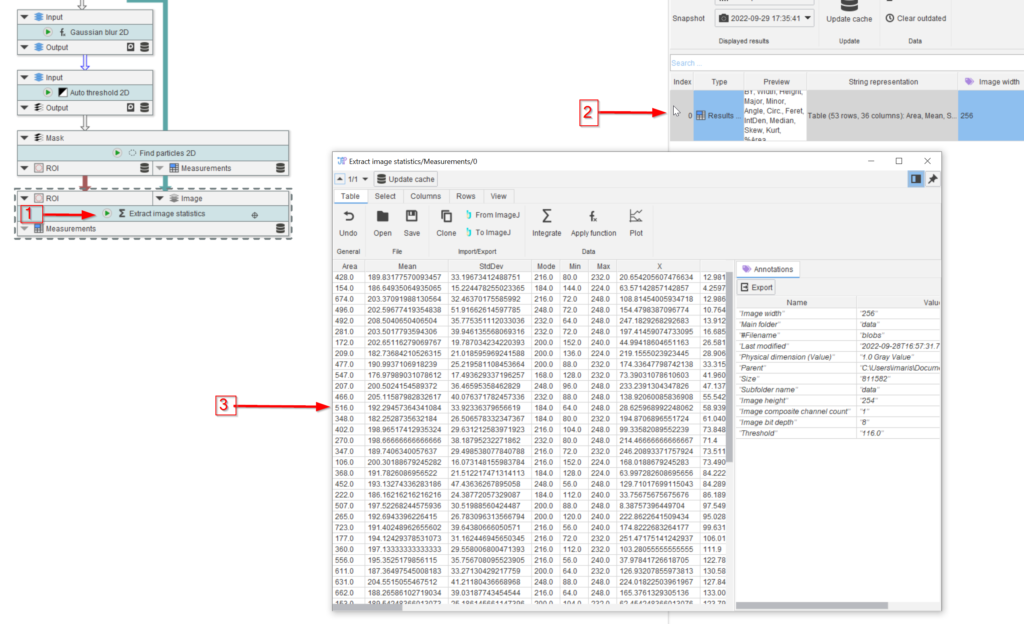
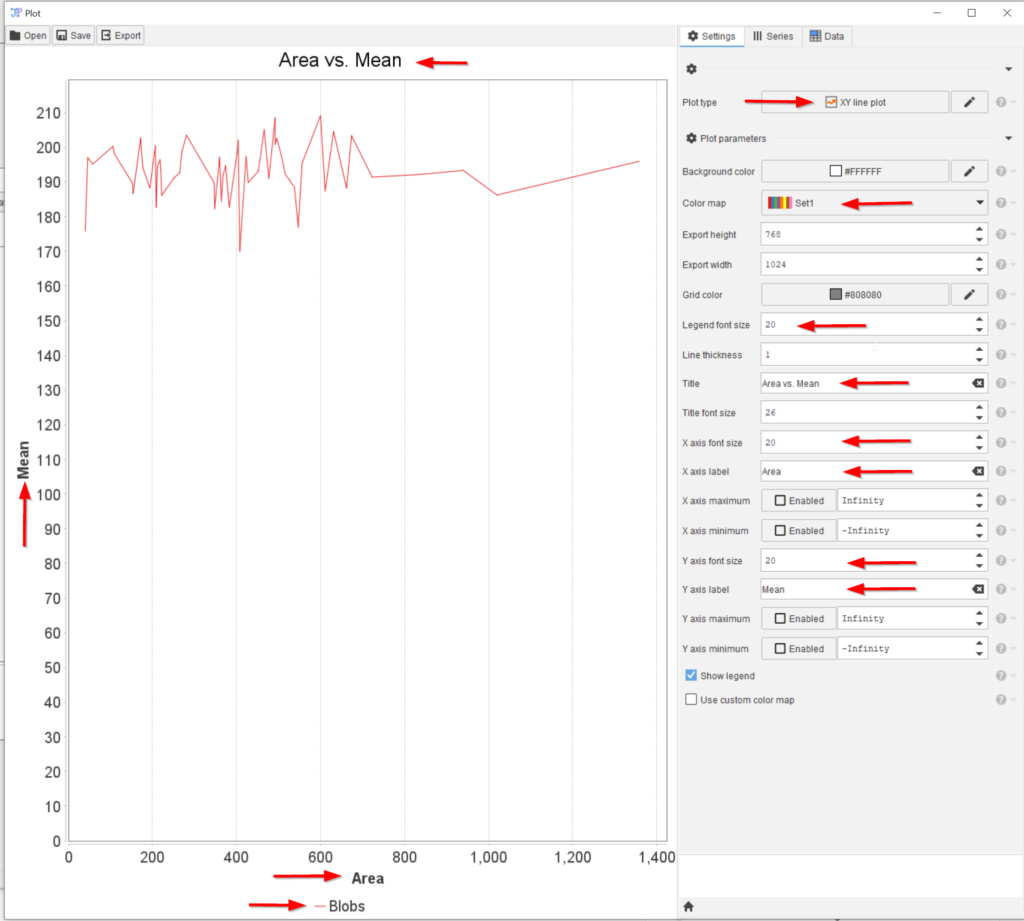
Plot the Mean values vs. the Area using the Table’s plot function, as shown in a tutorial before.
The red arrows show the settings that were changed from the default values view the plot window.
Step 8
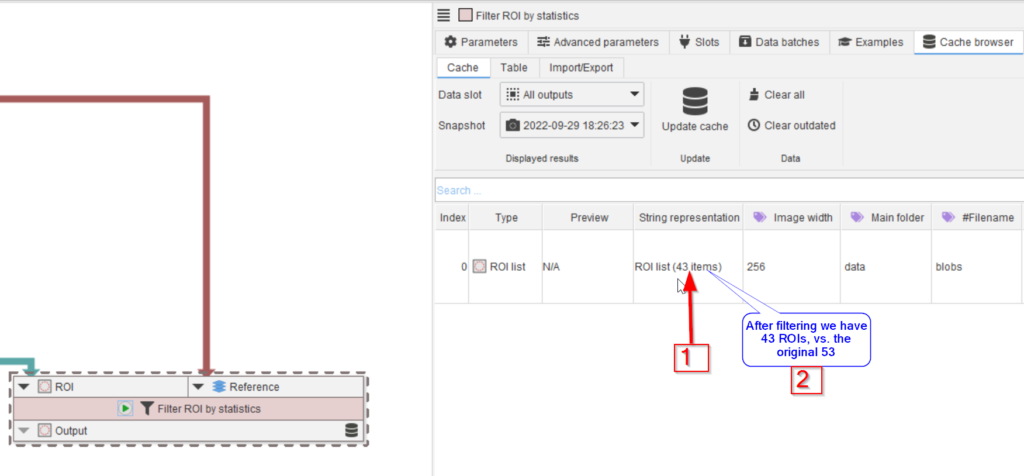
From this plot it appears that areas below 150 and above 700 are rare. We can ignore these values by filtering the ROIs.
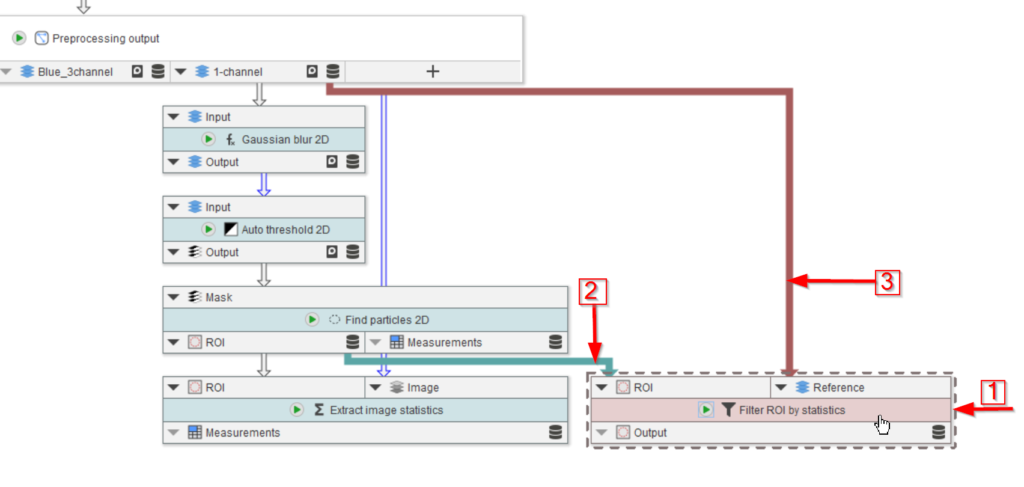
Look for such node via the top menu and navigate to ROI (red arrow 1), then Filter (red arrow 2), and choose Filter ROI by statistics (red arrow 3).
Step 10
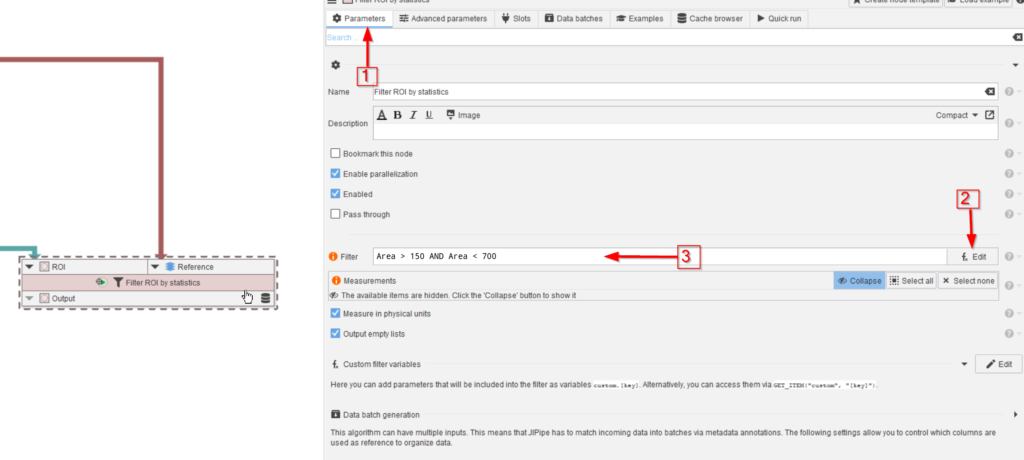
Go to the Parameters tab of the Filter ROI by statistics node (red arrow 1) and use the expression editor (red arrow 2) as shown before to create the filtering formula (red arrow 3):
Area > 150 AND Area < 700Step 12
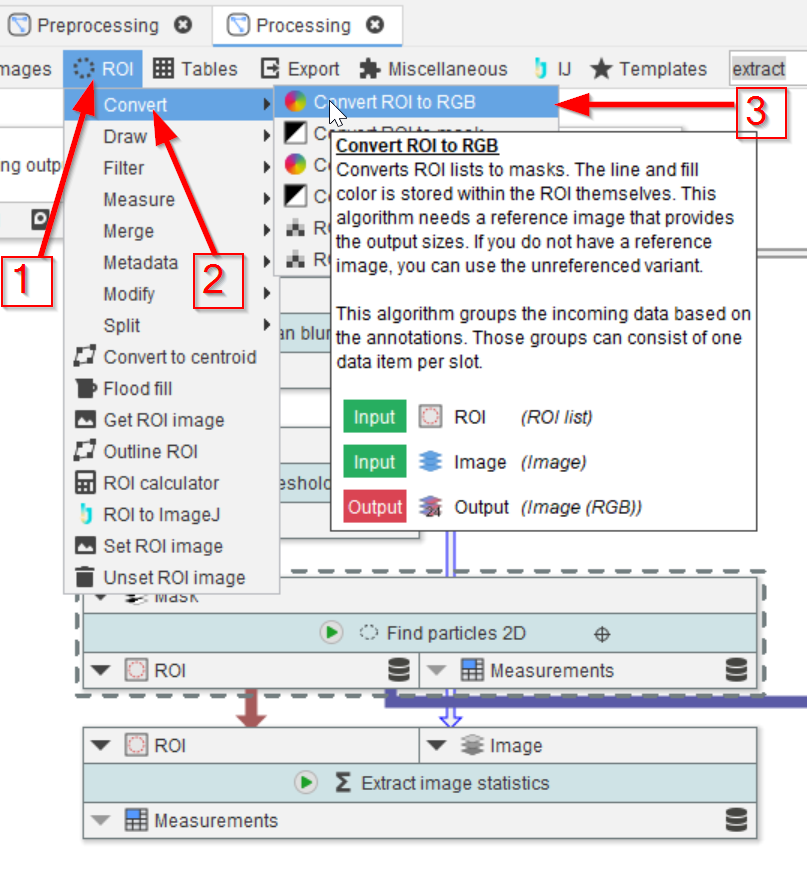
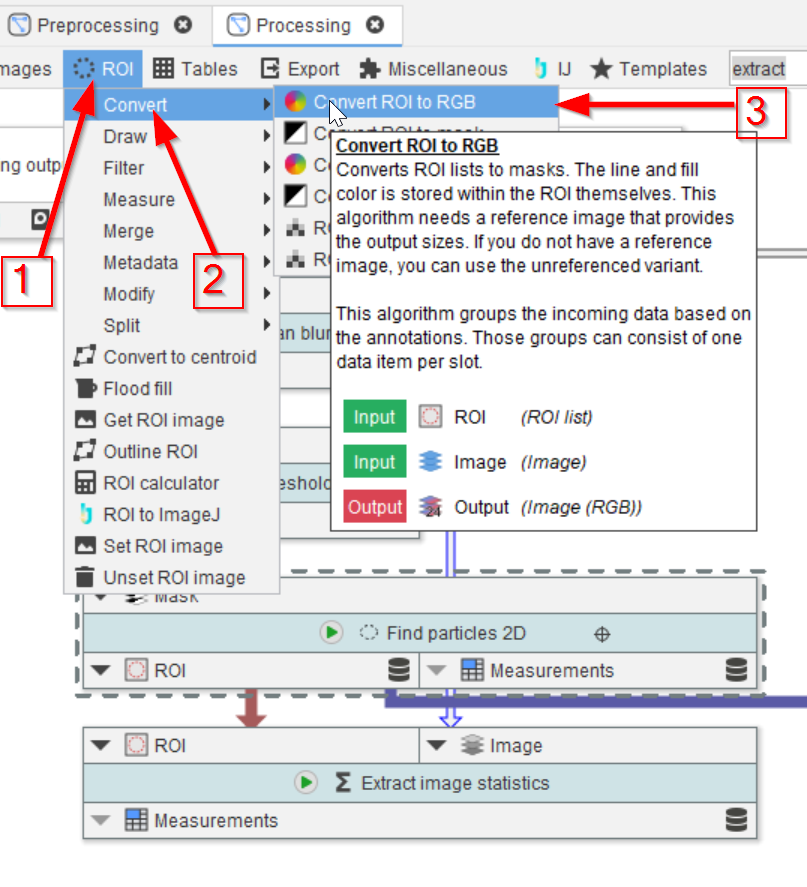
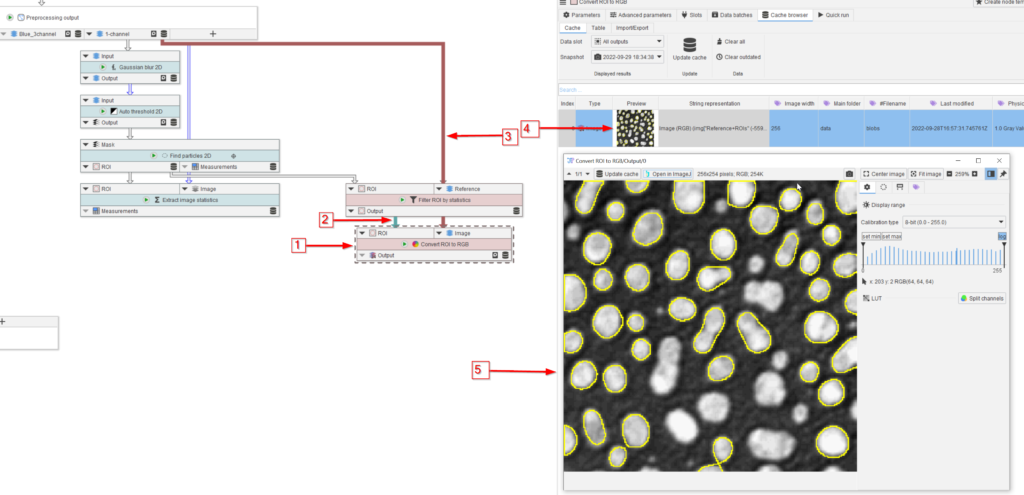
We now plot the selected ROIs in an overlay image with the original 1-channel data. Browse the ROI menu (red arrow 1) to look for Convert functions (red arrow 2), and select the Convert ROI to RGB function (red arrow 3).
Step 13
Add the node to the UI (red arrow 1), connect it to the filtered ROI list (red arrow 2) and to the 1-channel image (red arrow 3).
Run the node and observe the cache entry (red arrow 4) and the full image in a viewer (red arrow 5). The exclusion of the very small and very large ROIs can be observed.
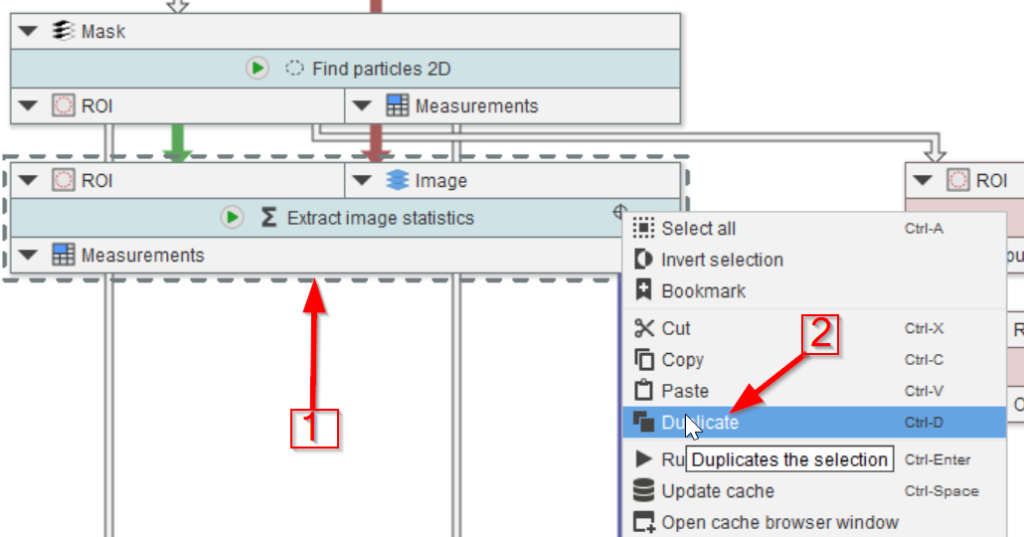
Step 15
Connect the duplicated node to the filtered ROI output (red arrow 1) and to the 1-channel image (red arrow 2).
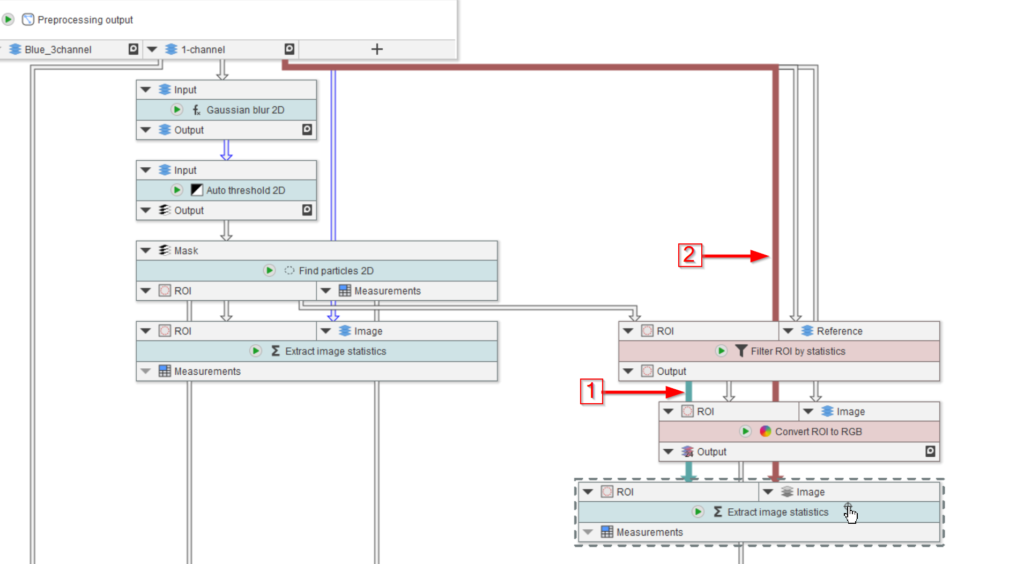
Create two new input nodes on the Processing compartment output node: one for the filtered ROI measurements, and one for the ROI overlay image.
Connect the old output slots (red arrows 1-3), as well as the two new ones to the output node (red arrow 4-5).
Now the statistics are extracted from filtered ROIs.