Deep Learning
JIPipe provides Deep Learning support via a standardized Python interface that allows to train/segment with different networks.
Setting up Deep Learning
Deep Learning requires a Python installation that comes with Tensorflow 2. To simplify this process,
we included automated installers for this environment that can be accessed via Project > Application settings > Extensions > Deep learning.
Here, click Select/install at the Tensorflow item.
The installer will ask you to review various settings - these should be fine for most system configurations.
If you are more experienced, then you can change the settings accordingly. You can also select an existing Conda or virtualenv
environment by choosing the Additional compatible installers section inside Select/Install.
GPU processing requires large amounts of VRAM. You can always disable GPU processing on a per-node basis if your hardware is not sufficient.
Especially on Windows, the installation of the GPU version takes a considerable time (30 min +). Due to buffered text output, you might not always receive progress info from the Conda installation process. We cannot fix this on our end.
nvidia-cuda-toolkit (please review the output of APT carefully, as nvidia-cuda-toolkit only works with specific driver versions).
On Windows, download the CUDA toolkit from the Nvidia homepage. Please restart JIPipe or Windows after installing the toolkit -
otherwise the installed files will not be found by Tensorflow.
Training
To train a network from scratch, add a Create model node into the pipeline and set it up. It allows you to choose from
different architectures and setup the expected image size, the number of classes, and additional factors like the
learning rate. Here you also have to decide which kind of model is created: For example you can create segmentation oder
classification models.
Depending on the model choice, you will need to prepare your data in different ways:
Segmentation models
Segmentation models are trained on labeled images, where the label is in most cases a binary mask.
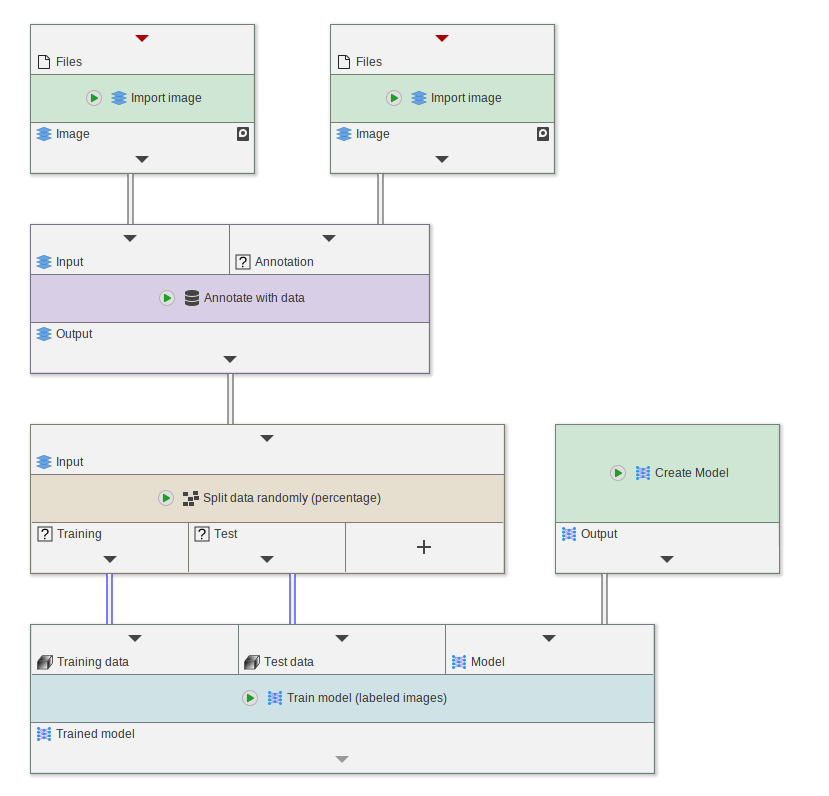
The label must be annotated as data annotation to the raw image (for example via the Annotate with data node).
The data is supplied to the Train model (labeled images) node, which has three inputs:
- Training data: This contains the labeled images that are used for training the network
- Test data: This contains labeled images for evaluating the performance of the network
- The model (created from
Create modelor a pretrained model)
Please always ensure that there is no data shared between training and test data to prevent overfitting.
You can achieve this either manually or by using the Split data randomly (percentage) node.
Classifier models
Classifiers determine which kind of object is shown in the image.
